Polygon: Sweeping Global Brands Off Their Feet and Into Web3
The Ethereum scaling solution (and more) bringing the likes of Nike, Starbucks, Meta, Adidas, Disney, and more into the Web3 world.
Welcome to the latest edition of ‘The API Economy’ — thanks for reading.
To support The API Economy, be like one of the 2,903 early, forward-thinking people, who subscribe for monthly-ish insights on the API economy, crypto, blockchains, and more emerging trends.
In 2023, we’ve seen the world’s biggest brands continue to invest in Web3 projects as global lawmakers work on better regulatory frameworks, the NFT market gets back on its feet after a brief hiatus, and Bitcoin makes a surprise run in March (we’re back, baby!)
To meet growing demand, however, the blockchain industry has had to face one of its biggest challenges to date: scalability. Most notably, as Ethereum has ballooned in growth, developers who work on Ethereum have had to ask themselves, “how do we keep our network fast, efficient, and secure?”
That’s where Polygon comes in.
At its core, Polygon is a Layer 2 scaling solution for Ethereum that aims to improve its speed, security, and affordability. With lower transaction fees, faster confirmation times, and the ability to support decentralized applications (dApps), Polygon has quickly gained popularity among crypto enthusiasts and investors.

According to data from Nansen, The number of daily transactions on Polygon surpassed Ethereum transactions in May 2021 and has since eclipsed Ethereum’s daily transaction number with almost 4x as many transactions per day.
Beyond raising $450 million from investors last year, some of the world’s biggest brands (including the likes of Coca-Cola, Starbucks, and Nike) are partnering with Polygon as a blockchain technology service provider. Polygon has become an extremely attractive solution for global giants that want to launch large-scale Web3 projects like NFT marketplaces, where high transaction volumes are expected.
Polygon is also making waves in the gaming industry, including a new alliance with the Web3 gaming firm Immutable to accelerate innovation and adoption in the crypto gaming space. On top of that, the massive South Korean gaming studio Nexon just announced that they will be launching the popular NFT game MapleStory Universe on a dedicated Polygon supernet.
In February of 2023, Polygon outperformed both Ethereum and Bitcoin, largely thanks to skyrocketing rates of adoption and interest over the past few months. Its price has seen some volatility since then, but it remains a strong player in the market.

And as of last week, Polygon launched Polygon zkEVM beta (we’ll get more into this later) showcasing their continued dedication to bringing Ethereum to everyone.
In this essay, we’ll explore the technology behind Polygon, why the biggest brands in the world are partnering with Polygon and its potential impact on the entire digital landscape.
Ogres have layers, crypto has layers
To truly understand Polygon, we first need to understand Ethereum — and its issues.
Ethereum is a decentralized blockchain platform that allows developers to build and deploy decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts. When you look at market capitalization, it is the second-largest cryptocurrency following Bitcoin.
However, as cryptocurrency has become more mainstream, Ethereum has faced a number of scalability issues. The Ethereum network can only handle a limited number of transactions per second, which can lead to slow confirmation times and high transaction fees during periods of high network usage.

For example, during the height of the DeFi craze in 2020, the Ethereum network experienced significant congestion due to the high number of transactions being processed by popular dApps such as Uniswap and Compound. As a result, transaction fees on the Ethereum network skyrocketed, with users paying as much as $100 or more to make a single transaction.
Confirmation times also increased, with some transactions taking hours or even days to be confirmed due to the network's limited throughput capacity. This made it difficult for many users to participate in the DeFi ecosystem and highlighted the need for scalable solutions such as Polygon.
In ‘Own the internet’, Not Boring founder Packy McCormick writes:
“third-party Layer 2 solutions, like Polygon are already working to speed up transactions and lower fees by essentially batching transactions off-chain and settling on-chain in one transaction instead of many (there are intricacies, but this is close enough). L2 solutions could increase throughput another 100x, and combining Eth2 and L2 solutions could lead to a 10,000x improvement if the theory plays out in practice.”
Polygon aside, Ethereum has been working on several of its own solutions, including sharding and more recently, danksharding. Sharding is a complex process that involves splitting the network into smaller parts called "shards," each of which can process transactions independently. Danksharding is still a rather theoretical solution but Ethereum developers hope it will be even more secure and decentralized than sharding, allowing Ethereum to continue to scale.

Until these solutions are fully implemented, however, Ethereum has also been relying on Layer 2 scaling solutions, which allow for faster and cheaper transactions by processing them off-chain and then settling them on the Ethereum network.
Polygon is one of the more popular of those Layer 2 scaling solutions. Essentially, Polygon allows developers to create and deploy their decentralized applications (dApps) on a separate network that is connected to Ethereum.
By doing so, Polygon provides faster and cheaper transactions, as the majority of transactions are processed on Polygon's network, and only the final results are committed to the Ethereum blockchain. This allows for a significant increase in the number of transactions that can be processed, with Polygon's network capable of handling up to 7,000 transactions per second (vs. Ethereum’s 20 tps).
Ethereum vs. Polygon: what’s the difference?

Think of the main blockchain network (including Ethereum) as a highway with a limited number of lanes. Just like a highway, when there is too much traffic on the network, it can become congested, and transactions can slow down or even come to a complete stop.
Now imagine a parallel road next to the highway that allows some of the traffic to bypass the congestion on the highway. This parallel road could have more lanes and be designed specifically to handle a larger volume of traffic, making it faster and more efficient.
In the same way, a Layer 2 solution is like a parallel road next to the main blockchain network. It processes some of the transactions off-chain, which allows it to handle a larger volume of transactions without slowing down the main network. When the off-chain transactions are settled on the main network periodically, it's like the traffic from the parallel road merging back onto the main highway.
This way, Layer 2 solutions can help to alleviate congestion and improve the speed and efficiency of the overall network, without compromising the security or decentralization of the blockchain.
Why Polygon is essential in an increasingly Web3 world

To understand why scaling solutions are crucial to the future of cryptocurrency, we should take a brief look at dApps.
The term "dApp" refers to a type of application that runs over a decentralized network, such as a blockchain, rather than on a centralized server. Using them is similar to using regular apps on your smartphone or computer, but with a few key differences.
In a traditional app, a central authority or company controls the app's data and operations. This centralization can lead to issues like censorship, data breaches, or limited access to services. On the other hand, dApps distribute control across multiple computers, or "nodes," in a decentralized network, making them more resistant to censorship, tampering, and single points of failure.
dApps are built for various purposes, including finance and gaming, and are important because they provide decentralized alternatives to traditional applications — offering users more security, transparency, and control.

For example, you may have heard of the popular dApp Uniswap, hosted on Ethereum. This dApp “enables users to trade cryptocurrencies without any involvement with a centralized third party” according to Investopedia.
According to some thought leaders, 2023 is slotted to be the year of dApps. Tony Cheng writes for Coindesk, “While 2022 saw some of the most unprecedented unravelings in crypto history, the fact of the matter is Web3 technology still has the opportunity to fundamentally change consumer behavior. Due to an emphasis on infrastructure throughout 2022, crypto is now at the phase where it is not lacking for infrastructure options. As we look ahead to 2023, what crypto needs is applications that will encourage user adoption and pave the way for Web2's transition to Web3.”
Which brings us to the question: why is Polygon such a big deal? Well, it’s in a perfect position to absolutely revolutionize dApp development by making the process faster, more efficient, and cheaper. Polygon is addressing the problems developers have with Ethereum and enabling a more efficient and accessible environment for building and using dApps.

But the benefits of Polygon go much further than just dApps — we’ll get into that in the sections below.
Where did Polygon come from?

Polygon (formerly Matic Network) was founded in 2017 by a team of experienced blockchain developers and entrepreneurs, including Sandeep Nailwal, Jaynti Kanani, and Anurag Arjun (who now runs Avail).
Known as Matic Network at the time, the team initially aimed to address issues like slow transaction speeds and high costs, both of which limited the usability of dApps built on the Ethereum blockchain.

Throughout 2018, the founding team worked to create a scalable sidechain and to simplify the process of building and deploying dApps on the platform. They established several strategic partnerships and collaborations during this time, such as working with Decentraland, a decentralized virtual reality platform, to provide scaling solutions. These collaborations helped Matic Network gain traction and credibility in the blockchain ecosystem.
By early 2019, Polygon had launched a beta version of its mainnet. During this beta phase, Polygon focused on demonstrating its capabilities as a Layer 2 scaling solution for Ethereum. The platform showcased its potential to provide faster and cheaper transactions using its sidechain architecture, relying on the Plasma framework and a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism.
The beta launch also allowed developers to build and deploy decentralized applications (dApps) on the platform, experiment with various scaling techniques, and test the network's performance and security features.
In June 2020, Polygon fully launched its mainnet to address a major bottleneck in the blockchain industry: scalability. The platform’s user base quickly ramped up from there.
As we mentioned before, networks like Ethereum are powerful tools — but they just aren’t ready for the high transaction volumes and demand they face today. This is partially why Polygon gained popularity so quickly, attracting a sizeable community of developers and users in just a few years.
Going mainstream with the world’s biggest brands
Polygon has had a remarkable journey in the past few years, becoming one of the most prominent players in the Ethereum ecosystem. They’ve attracted a diverse range of projects and users from various sectors, including gaming, DeFi, NFTs, and more.
And as more and more brands have become eager to join the Web3 craze, Polygon’s been there to support their efforts.
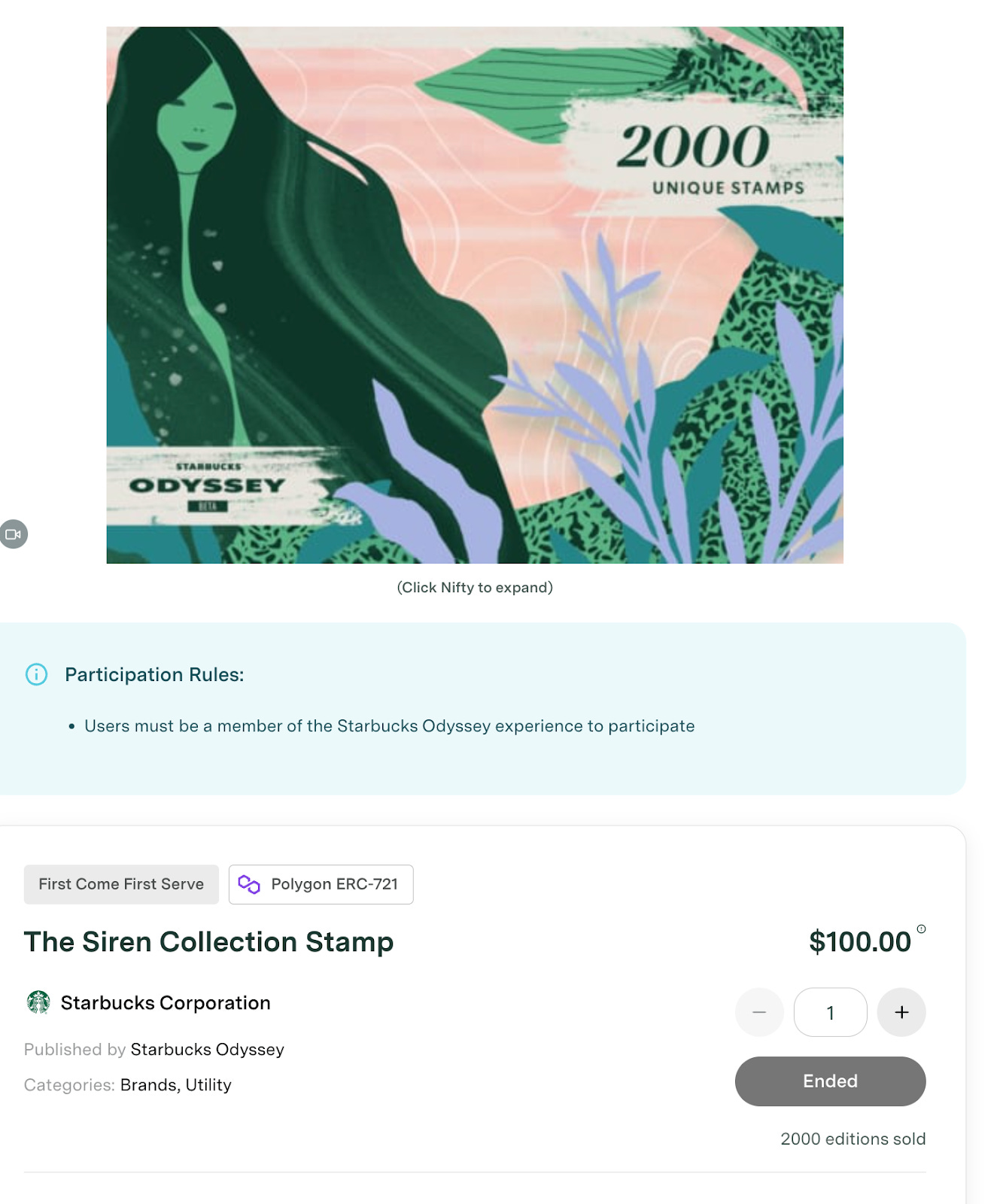
Polygon has secured several major partnerships with well-known brands and companies, including Starbucks. At the end of 2022, the coffee giant beta-launched a new NFT-based rewards program called Starbucks Odyssey — and they ended up selling 2,000 NFTs in just 20 minutes.
Since then, Starbucks has continued to roll out the program to customers that have joined the waitlist. Just a few weeks ago, with the help of Polygon, they launched a limited edition collection of “stamps” (NFTs) at $100 each. Once again, they sold out in under 30 minutes.
Members of Starbucks Oddysey can also complete online games like trivia to win more stamps. Some of those free stamps are now valued at over $1,000 on the secondary market. However, mainstream adoption of the program has been slow.
Polygon’s partnership with Nike has also been interesting to watch play out. Late last year, Nike announced they would be launching their first collection of NFT apparel, minted on Polygon.
Nike will be selling these NFTs on a new platform, .Swoosh, which will serve as the epicenter for Nike’s Web3 efforts — and will include future ways for customers to become co-creators and share in digital product royalties. .Swoosh will also allow users to unlock real-world benefits, such as exclusive physical apparel or chats with pro athletes using Web3 technology.
Nike originally announced that they would launch the platform in January 2023, but as of March 2023, it is still in a closed beta phase.

Prior to working with Polygon, Nike released some limited drops with digital apparel startup RTFKT, all of which were launched via the Ethereum mainnet. Nike hasn’t made a formal statement regarding why they chose Polygon for this new venture, however, it’s likely due to Polygon’s fast and affordable infrastructure.
Taking a look under Polygon’s hood
Polygon is shaking up the crypto ecosystem because it’s making Ethereum faster, cheaper, and more developer-friendly. It does this by creating a set of sidechains and shard chains that work together to handle more transactions at once, like adding more lanes to a highway to reduce traffic congestion.

The architecture of Polygon is composed of multiple components, including the Ethereum mainchain, the Heimdall Proof-of-Stake layer, and the Bor block production layer. Let’s break these down a little further:
Ethereum mainchain: Polygon's architecture relies on the Ethereum mainchain for certain functions, such as staking, checkpointing, and finality. This means that Polygon remains closely connected to the Ethereum ecosystem, benefiting from its security and network effects.
Heimdall (Proof-of-Stake layer): Heimdall is the validator layer of the Polygon architecture, which secures the network using a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus algorithm. Validators stake MATIC tokens on the Ethereum mainchain to participate in the network. Heimdall is responsible for the following tasks:
Proposer selection: Heimdall randomly selects a validator to propose a new block for the Bor block production layer, ensuring decentralization and security.
Checkpointing: Heimdall periodically submits a Merkle root of the latest block hashes to the Ethereum mainchain as a "checkpoint." This process anchors the Polygon sidechain to Ethereum's security, providing finality and preventing double-spending attacks.
Staking and delegation: Validators stake MATIC tokens to participate in the network, while delegators can support validators by delegating their tokens to them. This helps maintain the security of the network and provides an incentive for validators and delegators through block rewards and transaction fees.
Bor (block production layer): Bor is the block production layer in Polygon's architecture, where transactions are executed and blocks are created. It uses a consensus algorithm called Heuristic Merkleized Sharding (HMS) to group validators into multiple "shards" that validate and produce blocks in parallel. This design allows Polygon to achieve higher throughput and scalability compared to the Ethereum mainchain.

These three components work together to create a secure and scalable platform that can support a wide range of decentralized applications (dApps) and other Layer 2 solutions. By leveraging Ethereum's security and layering on additional scaling techniques, Polygon is solving some of the most pressing challenges faced by blockchain networks.
NFTs on Polygon

Polygon has gained a lot of attention as a popular platform for creating and trading non-fungible tokens (NFTs). The Polygon network provides a cost-effective and scalable solution for NFT creators and collectors, allowing them to avoid the high gas fees and slow transaction times that are often associated with Ethereum-based NFTs.
As one example, these lower transaction fees make smaller NFT transactions more accessible leading to L2s hitting all-time highs in March 2023 for a total share of Ethereum gas spend (see image below):
Polygon's interoperability with Ethereum-based NFTs also allows for easy migration of existing NFT projects to the Polygon network, and its decentralized network ensures that NFT ownership and transactions are secure and transparent.
The Polygon ecosystem has enabled new use cases for NFTs that were previously not feasible on other platforms. For example, the platform has been used for NFT-based gaming, where players can trade and collect unique in-game assets. Polygon-based NFTs have even been used for charitable purposes, such as raising funds for social causes or disaster relief efforts.
Polygon's scalability, low fees, and versatility have made it a popular choice for creators and collectors alike, driving the growth and innovation of the NFT market — and the popularity of Polygon leading to popular NFT projects like y00ts switching over to Polygon.

Solving the blockchain “trilemma”
Beyond NFTs, Polygon has become so popular because it has helped with many of the pain points associated with the infamous blockchain “trilemma.”
The blockchain trilemma, a term coined by Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin, refers to the challenge of simultaneously achieving decentralization, security, and scalability in a blockchain network. It suggests that optimizing a blockchain for all three properties is difficult, often requiring trade-offs.
Polygon addresses the blockchain trilemma by employing a multi-layer architecture and various Layer 2 scaling techniques to strike a balance between decentralization, security, and scalability.

Decentralization is maintained through the Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism in the Heimdall layer (which we discussed in the previous discussion). This allows multiple validators to participate in block production and validation.
Security is achieved by anchoring the Polygon sidechain to Ethereum through a checkpointing mechanism, where the Merkle root of the latest block hashes is periodically submitted to the Ethereum mainchain. This process leverages Ethereum's security while benefiting from the PoS consensus in the Heimdall layer to protect the network.
Scalability is addressed through the Bor block production layer, which uses Heuristic Merkleized Sharding (HMS) to increase transaction throughput. Additionally, Polygon's support for various Layer 2 solutions allows the network to scale according to specific use cases and demands.
By using this combination of techniques and architecture, Polygon seeks to create a platform that offers a balance between the key properties of the blockchain trilemma, providing a more accessible and scalable ecosystem for developers and users.
The many advantages of using Polygon
By now, you can probably see why developers around the world are adopting Polygon at rapid speed. Beyond answering the trilemma, we’ve boiled down the main benefits of Polygon into four key areas:
Increased transaction throughput and faster confirmation times
Lower transaction fees
Improved security through the use of PoS
Increased decentralization and accessibility for developers and users
Let’s take a closer look at each of these, get ready for a wall of text:
Increased transaction throughput and faster confirmation times
One of the primary advantages of Polygon is its ability to scale transaction throughput while maintaining fast confirmation times. By using various scaling techniques along with its block production layer (Bor) and Heuristic Merkleized Sharding (HMS), Polygon can process a higher number of transactions per second (TPS) compared to the Ethereum mainchain.
This results in faster confirmation times for users, leading to a more seamless and responsive experience when interacting with dApps built on Polygon.
Lower transaction fees
High transaction fees on the Ethereum mainchain can be a significant barrier to entry for many users and developers. Polygon's Layer 2 scaling solution addresses this issue by offloading transaction processing from the mainchain to its sidechain.
Since the sidechain has a higher transaction throughput, this results in significantly reduced fees for users. Lower transaction fees make it more economically viable for developers to build and deploy dApps, while also allowing users to interact with these applications without incurring high costs.
Improved security through the use of Proof-of-Stake (PoS)
Polygon's Heimdall layer utilizes a PoS consensus algorithm to secure the network. Validators stake their MATIC tokens to participate in the consensus process, which aligns their interests with the overall security of the network. In case a validator acts maliciously, their staked tokens can be slashed as a penalty.
PoS has several advantages over Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus, including reduced energy consumption, a lower risk of centralization due to specialized hardware requirements, and resistance to certain types of attacks (e.g., long-range attacks). Additionally, Polygon's checkpointing mechanism, which periodically submits the Merkle root of the latest block hashes to the Ethereum mainchain, provides additional security by anchoring the sidechain to Ethereum's PoW-based security.
Increased decentralization and accessibility for developers and users
Polygon's architecture promotes decentralization by allowing multiple validators to participate in the block production and validation process. This reduces the risk of centralization and ensures that no single entity can control the network.
Furthermore, Polygon's compatibility with Ethereum's development tools and infrastructure (e.g., Solidity, Web3.js, MetaMask) makes it easy for developers to build and deploy dApps on the platform. This accessibility, combined with lower transaction fees and faster confirmation times, creates a more inclusive and user-friendly environment for developers and users alike.
Use cases and real-world applications

Polygon and its endless benefits are redefining what’s possible across industries. To truly show the power of this innovative platform, let’s take a look at some real-world examples:
Tokenization

Tokenization is the process of converting physical or digital assets into digital tokens on a blockchain. When assets are represented as tokens, it becomes possible to streamline transactions, enhance security, and increase transparency.
All the benefits listed in the previous section, plus Polygon's unique architecture and design, make it an outstanding platform for tokenization. By solving many of the problems that come with Ethereum (the leading platform for token creation), Polygon has the potential to completely transform the way assets are managed, exchanged, and interacted with.
One such asset that Polygon is already touching is the digital bond. A digital bond is a type of debt security that is issued and managed on a blockchain, rather than through traditional, paper-based methods. They function similarly to traditional bonds but leverage the benefits of blockchain technology to enhance efficiency, transparency, and security.
In February 2023, the German industrial manufacturer Siemens issued a digital bond on Polygon’s public mainnet… a bond worth $60 million euros, to be exact. Although the bond was issued on-chain, Siemens opted to collect proceeds from investors through conventional banking channels (mainly due to the fact that the digital euro isn’t available yet).
Siemens spoke publicly about why they decided to leverage blockchain technology with this bond: “[Blockchain platforms] make paper-based global certificates and central clearing unnecessary. What’s more, the bond can be sold directly to investors without needing a bank to function as an intermediary.”
By moving away from paper-based bonds to blockchain-based digital bonds, Siemens has streamlined the bond issuance process, reducing administrative burdens, increasing transparency, and making transactions faster and more efficient.
Most importantly, this pioneering move highlights growing mainstream interest in leveraging blockchain technology for traditional financial processes — and the way Polygon is bound to play a part in the global shift to decentralized finance.

Siemen’s digital bond is also likely to inspire other corporations to explore similar avenues, leveraging the power of Polygon and blockchain technology to reshape the way capital is raised and managed in industries.
Polygon’s role in decentralized finance (DeFi) isn’t stopping here, though.
Recently, the DeFi infrastructure firm Swarm Markets announced the launch of tradable, DeFi-compatible stocks and bonds on the Polygon network. This innovative offering will bring popular stocks like Apple and Tesla, as well as two US Treasury bond ETFs, to the world of decentralized finance.
While these tokenized securities will not be available to US investors, they cater to both retail and institutional investors, with no minimum investment required. This initiative expands the range of assets accessible through DeFi, and Swarm Markets plans to add more stocks and other assets to their offering in the future, further bridging the gap between traditional and decentralized finance.
According to Swarm, “This is the first regulated decentralized exchange (DEX) available on the layer 2 solution, making it one of the cheapest and safest options for people wanting to access DeFi with investor protections.”
Daniela Barbosa, executive director of Hyperledger Foundation, also says, “Tokenizing a wide variety of assets – from equities and index funds to real estate and carbon credits – offers huge potential in terms of not only enhancing transparency, auditability, and efficiency but also access to people who otherwise might not be able to tap into traditional markets. Zooming out, if done at scale, these kinds of transactions are poised to make markets far more efficient.”
Investment bank Citi is betting on the blockchain-based tokenization of real-world assets to become the next “killer use case” in crypto, with the firm forecasting the market to reach between $4 trillion to $5 trillion by 2030 according to Cointelegraph.

Citi argues that blockchain tokenization would supersede legacy financial infrastructure because it is technologically superior and provides more investment opportunities in private markets. The technology negates the need for expensive reconciliation, prevents settlement failures, and makes tedious operations more efficient. According to Citi:
"digitally native financial asset infrastructure, globally accessible, operating 24x7x365 and optimized with smart contract and DLT-enabled automation capabilities, which enable use cases impractical with traditional infrastructure."
Ultimately, by enabling large-scale tokenization of various assets, Polygon's technology is well-positioned to make financial markets more efficient and inclusive, revolutionizing the way we interact with and invest in these assets.
Gaming and virtual worlds

Historically, developers have faced several challenges while building blockchain-based video games, particularly on networks like Ethereum:
Network congestion and high transaction fees: These significantly hinder the gaming experience by causing slow transaction times and making in-game actions expensive for players.
Limited scalability: This leads to performance bottlenecks and a suboptimal gaming experience with latency and capacity issues.
Complexity: The learning curve associated with developing on some blockchain platforms can be a barrier for developers who are new to the technology, slowing down the growth and adoption of blockchain-based gaming.
These challenges remain relevant, but according to VentureBeat, “2023 will be the year that blockchain games deliver quality and fun” — all thanks to Polygon.
And as VentureBeat predicted, Polygon has delivered as they recently announced that they will team up with Immutable on a gaming-focused zkEVM.
Urvit Goel, vice president of games at Polygon, said in the same VentureBeat article, “Specifically in gaming, 2023 will be the year that blockchain and gaming will be judged heavily on all of the promises that are being made about great games. We need to start seeing some of those games. There will be enough to start making a determination about quality. A lot of these builders in stealth mode haven’t launched a product yet.”
Polygon is on track to revolutionize the gaming industry by providing a scalable and cost-effective platform for developers to create engaging, blockchain-powered gaming experiences.

Among its many other benefits, Polygon enables seamless integration of decentralized, player-driven virtual economies, true ownership of in-game assets, and innovative play-to-earn models. This empowers gamers to monetize their skills and time, while also fostering a more interconnected gaming experience through cross-platform interoperability.
In addition, Polygon's developer-friendly environment, with support for popular Ethereum development tools, reduces the learning curve and encourages the creation of cutting-edge decentralized gaming applications. The platform also promotes community-driven development, allowing players and developers to collaborate and shape the evolution of games through decentralized governance. By addressing the obstacles faced by both gamers and developers, Polygon is paving the way for a more immersive, inclusive, and rewarding gaming ecosystem.
Zero-knowledge (ZK) scaling

Polygon recently announced the world’s first zero-knowledge (ZK) scaling solution — fully compatible with Ethereum. According to Polygon, “[This] ground-breaking development of zkEVM is set to dramatically improve the experience of using and building with Ethereum by providing scalability and lower transaction costs.”
So why does this matter? First, let’s talk briefly about zero-knowledge scaling as a concept.
Zero-knowledge scaling is an advanced cryptographic technique that leverages zero-knowledge proofs to increase the transaction throughput and privacy of blockchain networks. It enables the aggregation of multiple transactions into a single proof, which can be verified by the network without revealing the details of the transactions themselves. Ultimately, this reduces the amount of on-chain data and computation required, which improves scalability while preserving privacy.

Zero-knowledge scaling also enhances privacy by allowing transactions to be verified without revealing the details of the transactions themselves. This feature can be particularly valuable in applications that require a high degree of privacy and confidentiality, such as finance or identity management.
Polygon's zkEVM, specifically, is a groundbreaking development that has the potential to transform the blockchain industry. zkEVM enhances the scalability of the Ethereum network, allowing it to process a higher number of transactions per second and alleviating network congestion.
This improvement in transaction throughput will create a more seamless and efficient user experience, which is crucial for the continued growth and adoption of decentralized applications (dApps) and the Web3 ecosystem.
Moreover, zkEVM's ability to reduce transaction fees makes interacting with the Ethereum network more accessible and affordable for users and developers. This cost reduction can further encourage the adoption of blockchain technology and unlock new possibilities for various industries and use cases.
Identity verification and authentication

Polygon is uniquely positioned to revolutionize the way today’s identity management systems are built and deployed. By harnessing the power of blockchain technology, this platform offers a decentralized, secure, and privacy-preserving solution that can streamline the process of identity verification and authentication, making it more resilient to fraud and identity theft while enhancing user privacy and control over personal data.
Just weeks ago, Polygon publicly released its own decentralized identity solution called Polygon ID, powered by zero-knowledge cryptography. This product is groundbreaking and presents a unique way for individuals to verify their identities in a Web3 world.

“Polygon ID is private by default, offers on-chain verification and permissionless attestation. There is nothing in the digital identity space now that ticks all these boxes,” said Mihailo Bjelic, Polygon’s co-founder. “It is also a great showcase for how zero-knowledge proofs can help us create a better world.”
So what are the use cases? Like many Web3 projects, Polygon ID is still under development. But the vision includes a world where users can verify their identities without ever revealing sensitive information — you’d be able to get into a bar without showing your physical ID (and all the details contained there) and use your favorite websites without routinely providing your personal information.
All roads lead to Polygon

Polygon has emerged as a game-changing force in the blockchain and Web3 ecosystem, addressing the limitations of Ethereum and other platforms by providing a scalable, cost-effective, and developer-friendly solution.
Through its innovative architecture and commitment to solving the blockchain trilemma, Polygon has made it possible for an increasing number of brands, industries, and users to leverage the benefits of decentralization.
It’s clear how Polygon has the potential to bring in a world where the blockchain is integrated into our daily life — from our coffee habits to the ID we show to get into a bar. It’s already a top 4 blockchain in terms of the number of active wallet addresses:


As Web3 continues to gain traction and reshape the digital landscape, Polygon's role in empowering developers, businesses, and users is becoming increasingly critical. And if the trend continues and brands continue to build on Polygon, they have the opportunity to become the AWS of crypto.
Over a decade ago, Fortune 500 companies began building on the AWS platform, making it a crucial part of how they do business, which helped AWS become the most popular SaaS tool ever. If Polygon continues in this direction, it might just become an essential blockchain tool for companies who want to stay relevant in a Web3 world.
By fostering an environment where innovation can flourish, Polygon is paving the way for a more inclusive, secure, and efficient digital-first future.
Thanks for reading — until our next adventure.
Special thanks to my friend Haley Davidson for copy help & edits and Mama Schroeder for additional edits (any typos are on them 😊).
Disclaimer: The views in this essay are my own personal opinions and don’t necessarily represent the views of Polygon, those mentioned in this article, or anyone other than myself.











Listen to this article (33min) at https://playtext.app/doc/clgglwqq20014lg0grjjd21up